CYBER SECURITY
Things?
Cyber security is the set of technologies, processes and measures to protect the operation of information systems and the company's information assets (data) from threats of all kinds.
An adequate protection and safety management system guarantees:
- integrity, confidentiality, availability
of data, information and IT services.
THE MAIN THREATS

- Ransomware attacks: attacks in which cyber criminals take control of the victim's assets which they will only make available for a ransom.DDoS threats: attacks that prevent users of a network or system from accessing information, services and other resourcesMalware: malicious software designed to damage a device, alter its operation, or gain unauthorized access. Social engineering and phishing threats: threats that attempt to exploit human error or human behavior to access information or services. Data threats: attacks aimed at obtain unauthorized access to data or manipulate data to interfere with system behavior.
- Internet Threats: Attacks that affect the availability of the Internet. For example the so-called BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) hijacking or BGP hijacKing.Disinformation - bad information: intentional attack that consists in creating or sharing false or misleading information to manipulate public opinion.Attacks on supply chains: strategy with which it is attacked an organization by hitting the weak points of its IT supply chain (and not only!) with potential cascading repercussions. Cyberwar: attacks by hostile nations, criminal organizations or terrorists against the infrastructures and institutions of a state, to cause serious damage and loss of life.
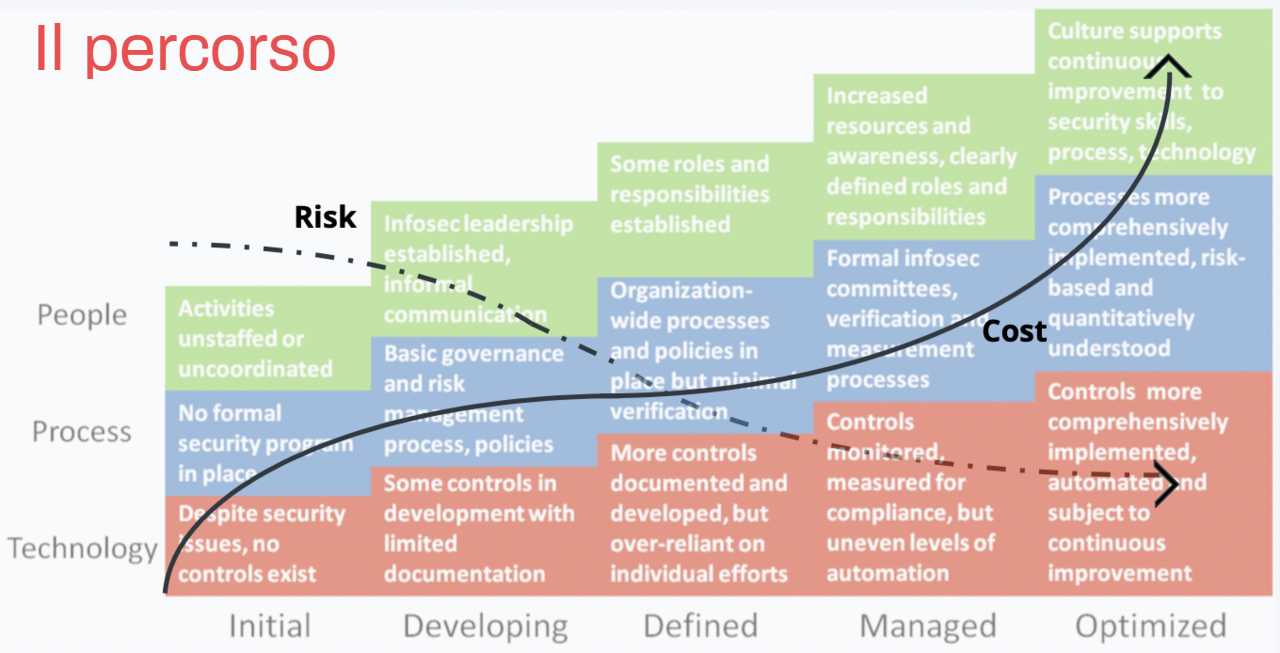
The phases of the journey
-
1. ANALYSIS
The analysis activities include:
-
2. PREVENTION/MITIGATION
This phase involves:
-
3. DISASTER RECOVERY PLAN IT (DRP)
The Disaster Recovery Plan presupposes that the IT services to be guaranteed have been identified and that a technological-organizational solution is actually available that allows the restoration of systems, applications and related infrastructures, guaranteeing the required RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective). .
-
4. IT SECURITY PROCEDURES
The intervention to adapt the processes and supporting documentation constitutes the natural completion of the activities begun with the analysis and involves the drafting of a procedural system that allows the company to formalize the main IT processes and to prepare the documentation necessary to manage constantly ensure the security and continuity of IT services and to ensure compliance with sector regulations.
-
5. CISO ADVISOR
It is an external support and assistance service for the Manager or Internal IT Security Contact or Management
-
6. CYBER SECURITY TRAINING
User training and awareness is developed in three areas:
-
7. MONITORING / IMPROVEMENT
The level of safety, obtained through Analysis, Prevention and Mitigation, is maintained over time thanks to the monitoring of the state of health and the improvement of organizational and technological measures.
The benefits

- Optimization of RTO and RPO (the main parameters for data recovery) Guarantee of operational continuity of systems Reduction of costs caused by interruptions (downtime) Protection of the company's reputation Control and optimization of the performance of your Disaster Recovery solution
- Definition of clear and effective actions to deal with an unexpected situation and guide the restoration of operations Granular management of necessary interventions Minimization of impacts on the performance of information systems
Unforeseen events?
Risks to prevent?
How to increase resilience?
Tell us your needs
Costlab srl | Via Mauro Macchi 58 20124 Milan | VAT number: 06052210967 | Privacy Policy Cookie Policy






